Treatment of Quadriceps Muscle Strain Injury (Front Thigh Muscle Pain):
Introduction
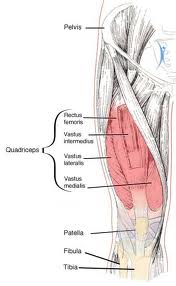
Strains of the quadriceps muscle usually occur during sprinting, jumping or kicking. Strains are seen in all the quadriceps muscles but are most common in the rectus femoris, which is more vulnerable to strain as it passes over two joints: the hip and the knee. The most common site of strain is the distal musculotendinous junction of the rectus femoris. Management of this type of rectus femoris strain and of strains of the vast muscles is relatively straightforward; rehabilitation time is short. Strains of the proximal rectus are not as straightforward and considered separately below.
Types of Quadriceps Muscle Strain
- Mild (Grade 1)
- Moderate (Grade II)
- Severe (Grade III)
Like all muscle strains, quadriceps strains may be graded into mild (grade 1), moderate (grade II) or severe, complete tears (grade III). The athlete feels the injury as a sudden pain in the anterior thigh during an activity requiring explosive muscle contraction.
There is local pain and tenderness and, if the strain is severe, swelling and bruising. Grade I strain is a minor injury with pain on resisted active contraction and on passive stretching. An area of local spasm is palpable at the site of pain. An athlete with such a strain may not cease activity at the time of the pain but will usually notice the injury after cooling down or the following day.
Moderate or grade II strains cause significant pain on passive stretching as well as on unopposed active contraction. There is usually a moderate area of inflammation surrounding a tender palpable lesion. The athlete with a grade II strain is generally unable to continue the activity. Complete tears of the rectus femoris occur with sudden onset of pain and disability during intense activity. A muscle fiber defect is usually palpable when the muscle is contracted. In the long term, they resolve with conservative management, often with surprisingly little disability.
Treatment of Quadriceps Muscle Strain
The principles of treatment of a quadriceps muscle strain are similar to those of a thigh contusion. They are also appropriate for the treatment of quadriceps strain; however, depending on the severity of the strain, progression through the various stages may be slower.
- Although loss of range of motion may be less obvious than with a contusion, it is important that the athlete regain pain-free range of movement as soon as possible.
- Loss of strength may be more marked than with a thigh contusion and strength retraining requires emphasis in the rehabilitation program.
- As with the general principles of muscle rehabilitation, the program should commence with low resistance, high repetition exercise.
- Concentric and eccentric exercises should begin with very low weights.
- General fitness can be maintained by activities such as swimming (initially with a pool buoy) and upper body training.
- Functional retraining should be incorporated as soon as possible.
- Full training must be completed prior to return to sport. Unfortunately, quadriceps strains often recur, either in the same season, or even a year to two later.
Differentiating between a Mild Quadriceps Strain and a Quadriceps Contusion
Occasionally, it may be difficult between a minor contusion and a minor muscle strain but the distinction needs to be made as an athlete with a thigh strain should progress more slowly through a rehabilitation program than should the athlete with quadriceps contusion. The athlete with thigh strain should avoid sharp acceleration and deceleration movements in the early stages of injury. Some of the features that may assist the clinician in differentiating. Diagnostic ultrasound examination may be helpful in differentiating between the two conditions.
| DIAGNOSTIC FEATURES | QUADRICEPS CONTUSION |
| Mechanism | Contact Injury |
| Pain Onset | Immediate or soon after |
| Location | Usually Lateral or Distal |
| Bruising/Swelling | May be obvious early |
| Effect of gentle stretch | May initially aggravate pain |
| Strength testing | No loss of strength except pain inhibition. |
| Behavior of pain | Improves with gentle activity. |
Active Physical Therapy provides best services .Our services include to physical therapy, occupational therapy, hand therapy, senior wellness, neurological rehabilitation, orthopedic rehabilitation, industrial rehabilitation and specialties including auto accident injuries / Trauma Cases, Work-related Injuries, Sports Injuries, Post Surgical Rehabilitation, Lower Back Pain, Shoulder Pain/ Injuries, , Arthritis, Bursitis/Tendonitis, Carpal Tunnel Syndrome, Knee and Ankle Injuries, Leg Pain, Lumbar Stabilization, Muscle Strains. We severe many locations. For More Information Call Now at : 301-498-1604